Apollo 11, First Moon Landing (USA 🇺🇸)
July 20, 1969
Mass for Mass: Should We Keep the Moon Balanced?
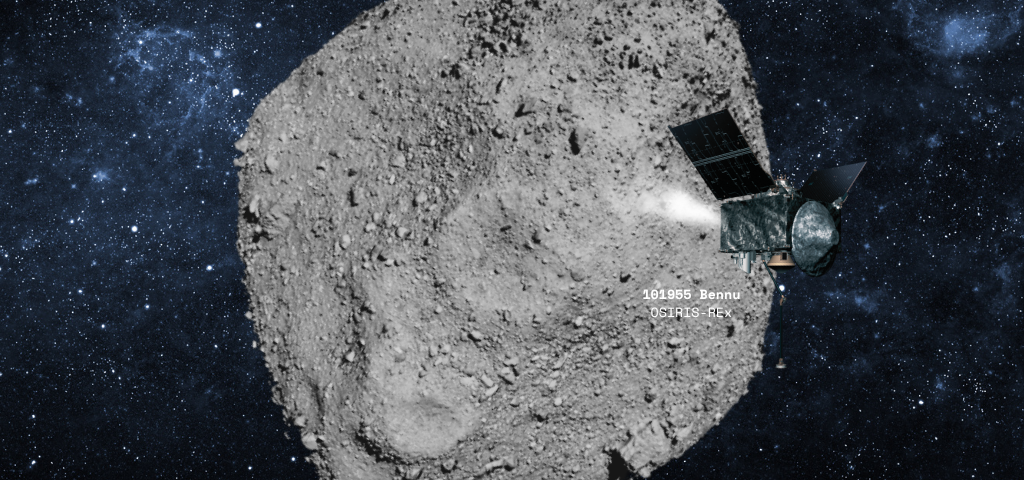
November 1, 2024The OSIRIS-REx mission, launched by NASA in 2016, represents a monumental leap in our quest to understand the origins of the solar system and the potential for resource utilization in space. This mission successfully collected samples from the near-Earth asteroid Bennu and returned them to Earth, paving the way for future endeavors in asteroid exploration and mining.
OSIRIS-REx Mission Overview
OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security, Regolith Explorer) was designed to travel to Bennu, a carbonaceous asteroid approximately 500 meters in diameter. The spacecraft launched on September 8, 2016, and arrived at Bennu in December 2018. After extensive mapping and analysis, OSIRIS-REx successfully collected samples from Bennu’s surface on October 20, 2020. The return capsule, containing these precious samples, landed in Utah on September 24, 2023. The mission has provided invaluable data on the composition and characteristics of Bennu, offering insights into the early solar system.
Current and Upcoming Asteroid Missions
Building upon the success of OSIRIS-REx, several missions are planned or underway to further explore asteroids:
- Tianwen-2 (China): Scheduled for launch in May 2025, this mission aims to collect samples from the near-Earth asteroid 469219 Kamoʻoalewa and return them to Earth. Following the sample return, the spacecraft will continue to study the comet 311P/PANSTARRS.
- Psyche (NASA): Set to launch in October 2023, the Psyche mission will explore the metallic asteroid 16 Psyche, believed to be the exposed core of a protoplanet. This mission will provide insights into planetary formation and the composition of metallic asteroids.
- Hera (ESA): Planned for launch in October 2024, the European Space Agency’s Hera mission will study the binary asteroid system Didymos and its moonlet Dimorphos. This mission will follow up on NASA’s DART mission to assess asteroid deflection strategies.
Implications for Business: Harvesting Asteroid Resources
The successful retrieval and analysis of asteroid materials have profound implications for the future of space-based industries:
- In-Space Resource Utilization: Asteroids contain water ice and other volatiles that can be converted into rocket fuel, life support resources, and radiation shielding. Utilizing these materials directly in space could significantly reduce the costs of deep-space missions by minimizing the need to launch supplies from Earth.
- Manufacturing and Construction: The minerals found in asteroids, such as nickel, iron, and cobalt, could be used for in-space manufacturing and construction. This capability would enable the building of large structures, habitats, and spacecraft in orbit, fostering the development of space infrastructure.
- Economic Opportunities: Asteroids are rich in precious metals like platinum and gold. Successfully mining these resources could lead to new markets and economic opportunities, potentially transforming the global economy. However, the influx of these materials would need to be managed to prevent market destabilization.
- Technological Advancements: The challenges of asteroid mining will drive innovation in robotics, automation, and remote operations. These advancements could have wide-ranging applications, benefiting industries beyond space exploration.
In conclusion, missions like OSIRIS-REx not only enhance our scientific understanding but also lay the groundwork for a burgeoning space economy. The ability to harvest and utilize asteroid resources could revolutionize space travel, making it more sustainable and economically viable, while also opening new frontiers for business and industry.