Exploring Careers in the Final Frontier: Top Space Industry Jobs for 2025
February 12, 2025
Book Review: Space to Grow – Unlocking the Final Economic Frontier
February 26, 2025The Artemis program represents NASA’s ambitious initiative to return humans to the Moon and establish a sustainable presence, serving as a stepping stone for future Mars exploration. Central to this endeavor is a robust collaboration between NASA and private industry, fostering innovation and efficiency in space exploration.
Historical Context and Program Evolution
Initiated in 2017, the Artemis program aims to land “the first woman and the next man” on the lunar south pole region by 2025. This mission marks the first step toward a sustainable lunar presence, laying the groundwork for a lunar economy and eventual crewed missions to Mars. The program builds upon previous efforts, notably the Constellation program, which was canceled in 2010 due to budget constraints. Artemis leverages existing technologies like the Orion Crew Exploration Vehicle and the Space Launch System (SLS), both integral to the program’s success.
Key Components of the Artemis Program
-
Orion Spacecraft: Designed for deep space missions, Orion will transport astronauts to lunar orbit and back, providing life support and emergency abort capabilities.
-
Space Launch System (SLS): As NASA’s most powerful rocket, the SLS is capable of sending Orion, astronauts, and cargo directly to the Moon.
-
Lunar Gateway: A planned space station in lunar orbit, the Gateway will serve as a staging point for lunar landings and a hub for scientific research.
Pivotal Business Partnerships
The Artemis program’s success hinges on strategic collaborations with private industry, reflecting a paradigm shift toward public-private partnerships in space exploration. Notable collaborations include:
-
SpaceX: In April 2021, NASA selected SpaceX’s Lunar Starship as the Human Landing System (HLS) for Artemis missions. This contract involves developing a variant of SpaceX’s Starship to transport astronauts from lunar orbit to the surface and back. The selection underscores SpaceX’s role in advancing lunar exploration through innovative spacecraft design.en.wikipedia.org
-
Blue Origin: In May 2023, NASA awarded Blue Origin a $3.4 billion contract to develop the Blue Moon landing system for the Artemis V mission. This project includes an uncrewed test mission followed by a crewed Moon landing in 2029, highlighting Blue Origin’s commitment to supporting NASA’s lunar objectives.en.wikipedia.org
-
Lunar Outpost: This Colorado-based company is developing the Mobile Autonomous Prospecting Platform (MAPP) rover and is one of three finalists to develop the Lunar Terrain Vehicle (LTV) for the Artemis program. Lunar Outpost’s involvement exemplifies the critical role of smaller enterprises in advancing lunar mobility and resource utilization technologies.en.wikipedia.org
-
Intuitive Machines: As part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, Intuitive Machines has developed the Athena lunar lander, aiming to deliver scientific instruments to the Moon’s surface. Despite challenges during recent landing attempts, the company’s efforts contribute to the broader goal of integrating commercial capabilities into lunar exploration. reuters.com apnews.com
Future Outlook
The Artemis program’s roadmap includes several pivotal missions:
-
Artemis I: An uncrewed test flight of the SLS and Orion spacecraft, successfully launched on November 16, 2022, and returned to Earth on December 11, 2022.en.wikipedia.org
-
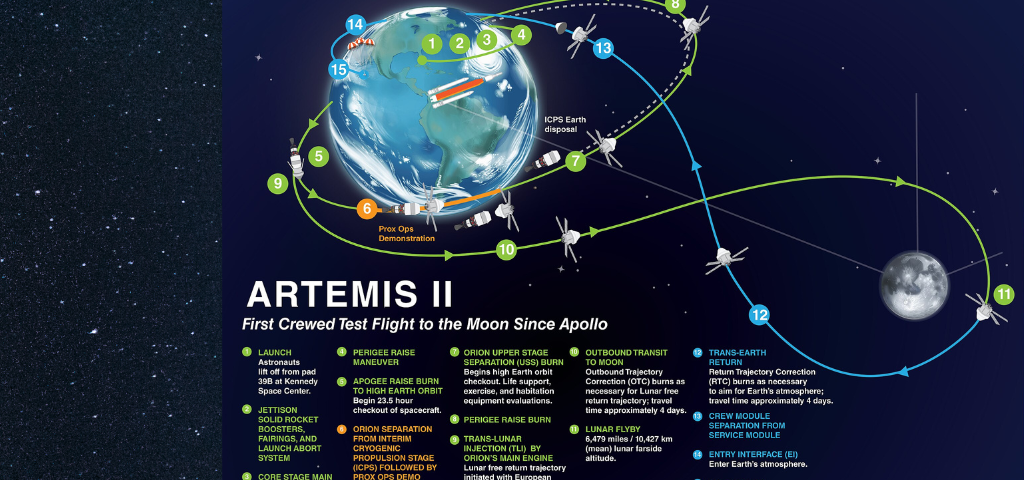
Artemis II: Planned for September 2025, this mission will be the first crewed test flight, sending astronauts on a lunar flyby to validate life support systems and crew performance.
-
Artemis III: Scheduled for no earlier than September 2026, this mission aims to achieve the first crewed lunar landing since Apollo 17, targeting the lunar south pole.
Subsequent missions, including Artemis IV and V, aim to establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon, facilitating scientific research and demonstrating technologies necessary for future Mars exploration. en.wikipedia.org
Implications for the Business Sector
The Artemis program’s emphasis on public-private partnerships has catalyzed growth in the commercial space sector. Companies involved in Artemis-related projects are poised to benefit from increased investment, technological advancements, and expanded market opportunities. The program’s success could stimulate further private sector participation in space exploration, leading to innovations in spacecraft design, lunar infrastructure, and resource utilization.
Moreover, the development of a lunar economy presents prospects for industries beyond aerospace, including mining, construction, and telecommunications. As NASA and its partners work toward a sustainable lunar presence, businesses across various sectors may find new opportunities in supporting and capitalizing on lunar exploration and habitation.
In conclusion, the Artemis program signifies a transformative era in space exploration, characterized by collaborative efforts between NASA and private industry. These partnerships are not only pivotal for achieving the program’s ambitious goals but also for fostering a vibrant commercial space ecosystem that could redefine business opportunities both on Earth and beyond.